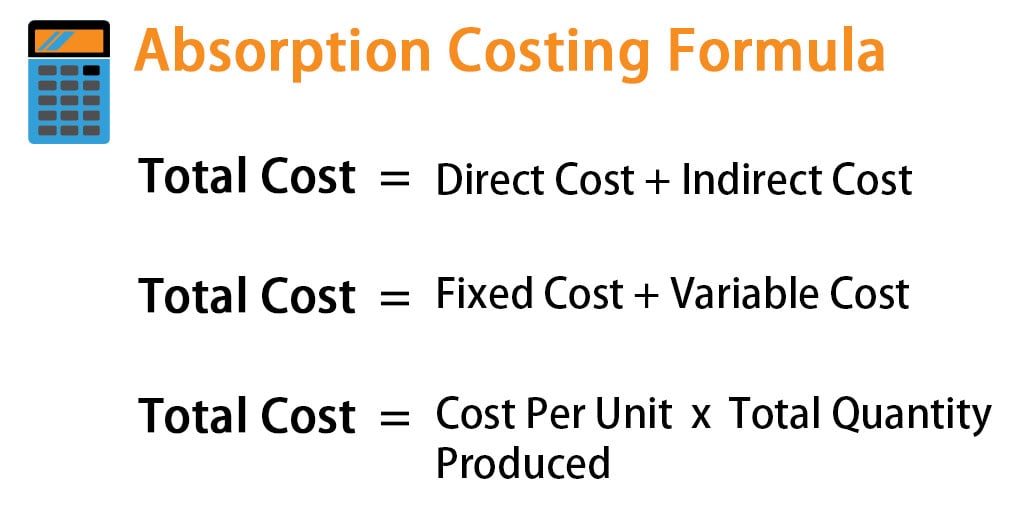
It includes direct costs such as direct materials or direct labor and indirect costs such as plant manager’s salary or property taxes. It can be useful in determining an appropriate selling price for products. Absorption costing and variable costing are two different methods of costing that are used to calculate the cost of a product or service. While both methods are used to calculate the cost of a product, they differ in the types of costs that are included and the purposes for which they are used. The differences between absorption costing and variable costing lie in how fixed overhead costs are treated.
What is absorption costing under GAAP?
But absorption costing net income is viewed as more accurate since it allocates all production costs. Revenue is recorded in the same way the irs says you have until july 15 to make 2019 ira or hsa contributions under both absorption costing and variable costing. It reflects the sales made during the period at the price agreed upon with customers.
- Carefully study the arrows that show how amounts appearing in the absorption costing approach would be repositioned in the variable costing income statement.
- Under absorption costing, companies treat all manufacturing costs, including both fixed and variable manufacturing costs, as product costs.
- It would be easy to use up full manufacturing capacity, one sale at a time, and not build in enough margin to take care of all the other costs.
Impact Of Inventory
Therefore, an absorption cost includes all direct and indirect costs, including labor, rent, insurance, etc. Since absorption costing includes allocating fixed manufacturing overhead to the product cost, it is not useful for product decision-making. Absorption costing provides a poor valuation of the actual cost of manufacturing a product. Therefore, variable costing is used instead to help management make product decisions. Absorption costing is a method of costing that includes all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, in the cost of a product. Absorption costing is used to determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory balances on the income statement and balance sheet, respectively.
Cost Accounting
Absorption costing “absorbs” all of the costs used in manufacturing and includes fixed manufacturing overhead as product costs. Absorption costing is in accordance with GAAP, because the product cost includes fixed overhead. Variable costing considers the variable overhead costs and does not consider fixed overhead as part of a product’s cost. It is not in accordance with GAAP, because fixed overhead is treated as a period cost and is not included in the cost of the product. While companies use absorption costing for their financial statements, many also use variable costing for decision-making.
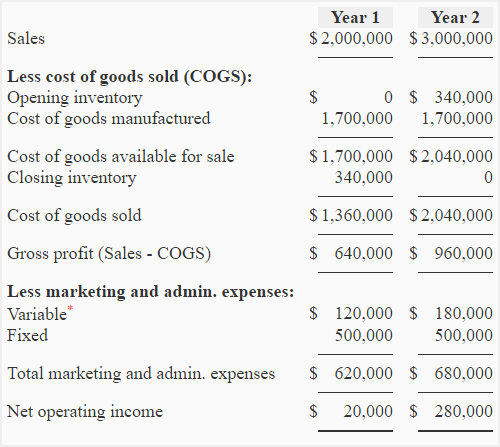
Reconciliation between absorption costing and variable costing
The Big Three auto companies made decisions based on absorption costing, and the result was the manufacturing of more vehicles than the market demanded. With absorption costing, the fixed overhead costs, such as marketing, were allocated to inventory, and the larger the inventory, the lower was the unit cost of that overhead. For example, if a fixed cost of \(\$1,000\) is allocated to \(500\) units, the cost is \(\$2\) per unit. While this was not the only reason for manufacturing too many cars, it kept the period costs hidden among the manufacturing costs. Using variable costing would have kept the costs separate and led to different decisions.
Please Sign in to set this content as a favorite.
It is also used to calculate the profit margin on each unit of product and to determine the selling price of the product. It’s important to note that period costs are not included in full absorption costing. In other words, a period cost is not included within the cost of goods sold (COGS) on the income statement. Instead, period costs are typically classified as selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expenses, whether variable or fixed. Advocates of absorption costing argue that fixed manufacturing overhead costs are essential to the production process and are an actual cost of the product.
This means the cost of ending inventory on the balance sheet is higher compared to variable costing methods. Absorption costing is a costing system that is used in valuing inventory. It not only includes the cost of materials and labor, but also both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead costs.
When an opening inventory is bigger than the closing inventory, the outcome would mean that the profits in absorption will be less due to a relatively higher amount of fixed cost in the former. Both variables costing and abortion costing may produce different profits due to different inventories valuation techniques. These profits only differ in the presence of an opening and closing inventory. Over the year, the company sold 50,000 units and produced 60,000 units, with a unit selling price of $100 per unit.